
At the end of this lesson-
1. You will be able to explain the concept of data communication medium.
2. You will be able to describe the types of wired medium.
3. You will be able to describe the twisted pair cable.
4. You will be able to describe the Co-axial cable.
5. You will be able to describe the fiber optic cable.
Go for Bangla Version
What is Medium?
Physical path through which data is transferred by establishing a link between sender and receiver is called medium. There are two types of medium:
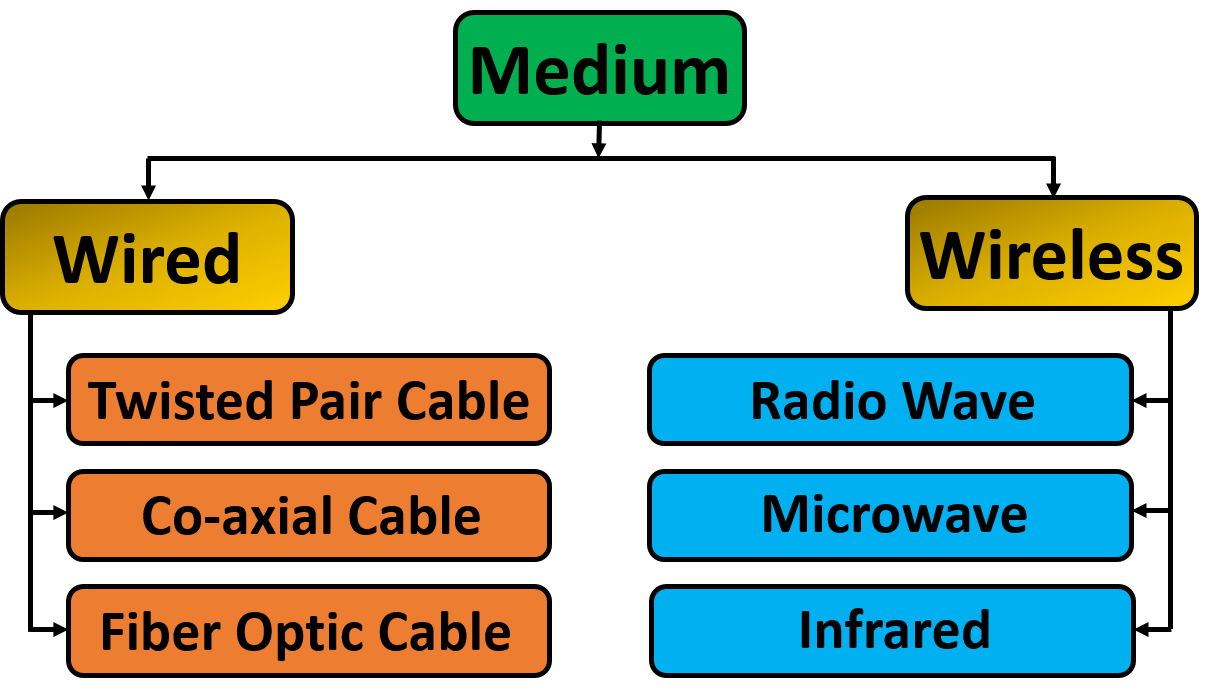
What is Channel?
Specific wave frequency or wire connection which is used to establish a link between sender and receiver for data transmission is called channel.
What is Wired Medium?
It is defined as the physical medium through which the signals are transmitted. It is also known as Bounded media.
- Twisted Pair Cable
- Coaxial Cable
- Optical Fiber Cable
What is Twisted Pair Cable?
A type of cable that consists of two independently insulated copper wires which are twisted together and run in parallel. The copper wires are typically 1mm in diameter. One of the wires is used to transmit data and the other is the ground reference.
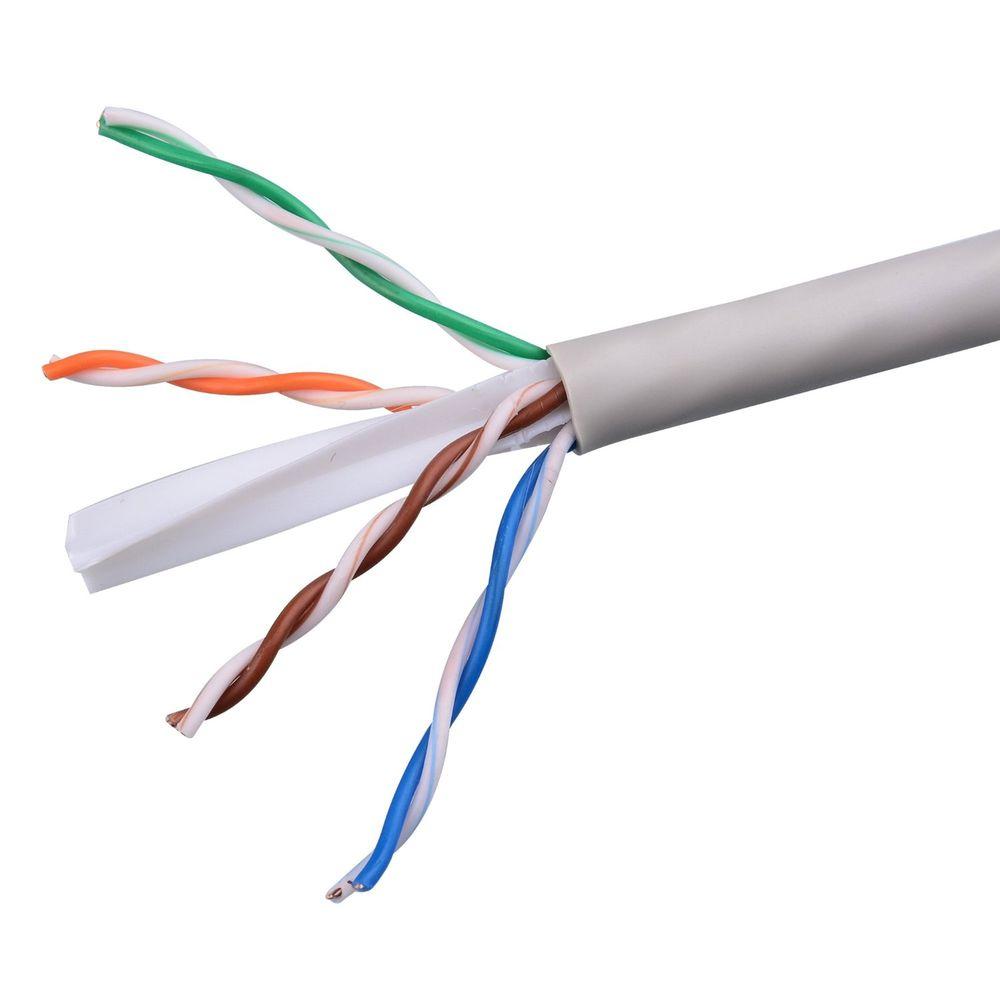
This type of cable usually uses a total of 4 pairs of wires. Each pair of 4 pairs has a common (white) color wire and a different color (orange, green, blue, brown) wire. For color coding, each pair has one white and another one of a different color. The number of twists per meter of four pairs of wires varies to reduce the crosstalk.
Reason for Twisting:
All transmissions are prone to noise, interferences, and crosstalk. When the wires are twisted, some part of the noise signals is in the direction of data signals while the other parts are in the opposite directions. Thus the external waves cancel out due to the different twists. The receiver calculates the difference in the voltages of the two wires for retrieving data. Thus a much better immunity against noise is obtained.
Connection of twisted pair cable is provided with RJ45 connector.
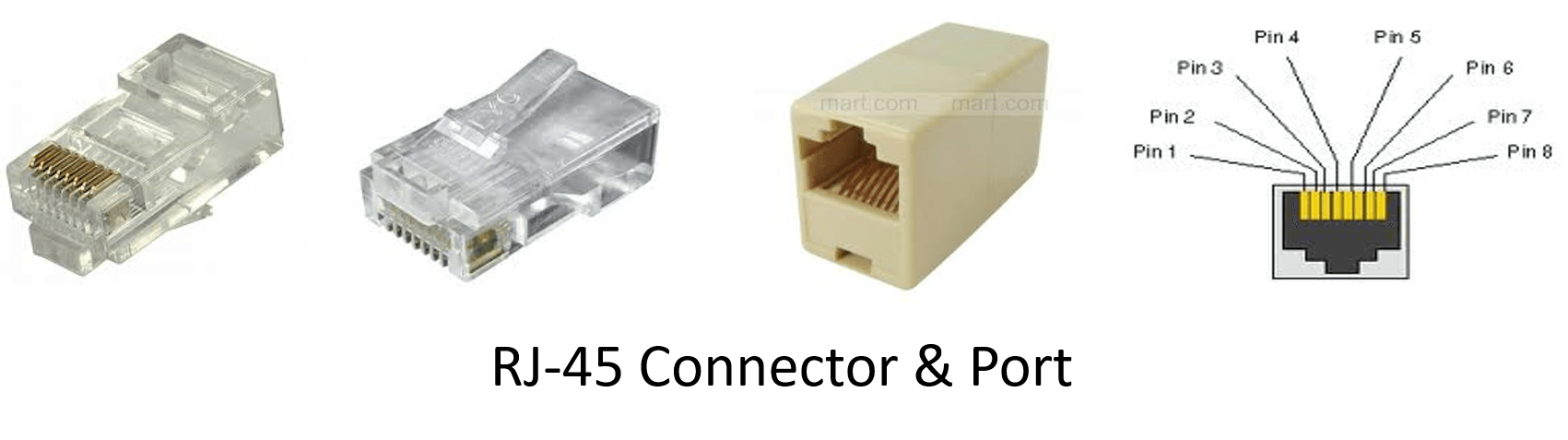

Types of twisted pair cable
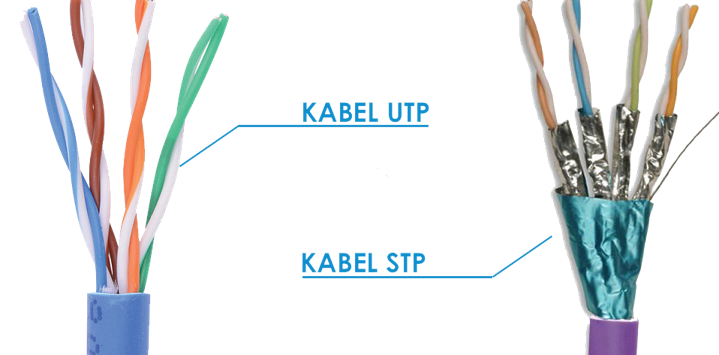
There are two types of twisted pair cables based on the presence and absence of shields:
Shielded twisted pair (STP):
‘Shielded’ with a foil jacket to cancel any external interference. Commonly used for large-scale enterprises for high-end applications as well as exterior cabling that may be exposed to environmental elements.
Transmission Speed: 16Mbps
Transmission Distance: 100m
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP):
‘Unshielded’ meaning it does not rely on physical shielding to block interference. Most commonly used cable of the two, often utilized for both residential and business use
Transmission Speed: 10Mbps
Transmission Distance: 155 m
Advantages of Twisted Pair Cable:
- Less costly and easy to install.
- Can be used for both analog and digital signal.
- This cable is widely used for short distance communication.
Disadvantages of Twisted Pair Cable:
- For every unit of length transmission delay increases and data transfer rate decreases.
- Transmission loss is very high.
- Can be used for communication at 100 meter distance only.
Uses of Twisted Pair Cable:
- Used in telephone system.
- Used in Local Area Computer Network.
What is Coaxial Cable?
In these cable there are two conductive layers which share the same axis. Thus this cable is called co-axial cable. Coaxial cables are high-frequency transmission cables made up of two conductive and two non-conductive parts. Data is transferred electrically over the inner conductor and has 80X more transmission capacity than twisted pair cables.
There are four parts in this cables. Such as:
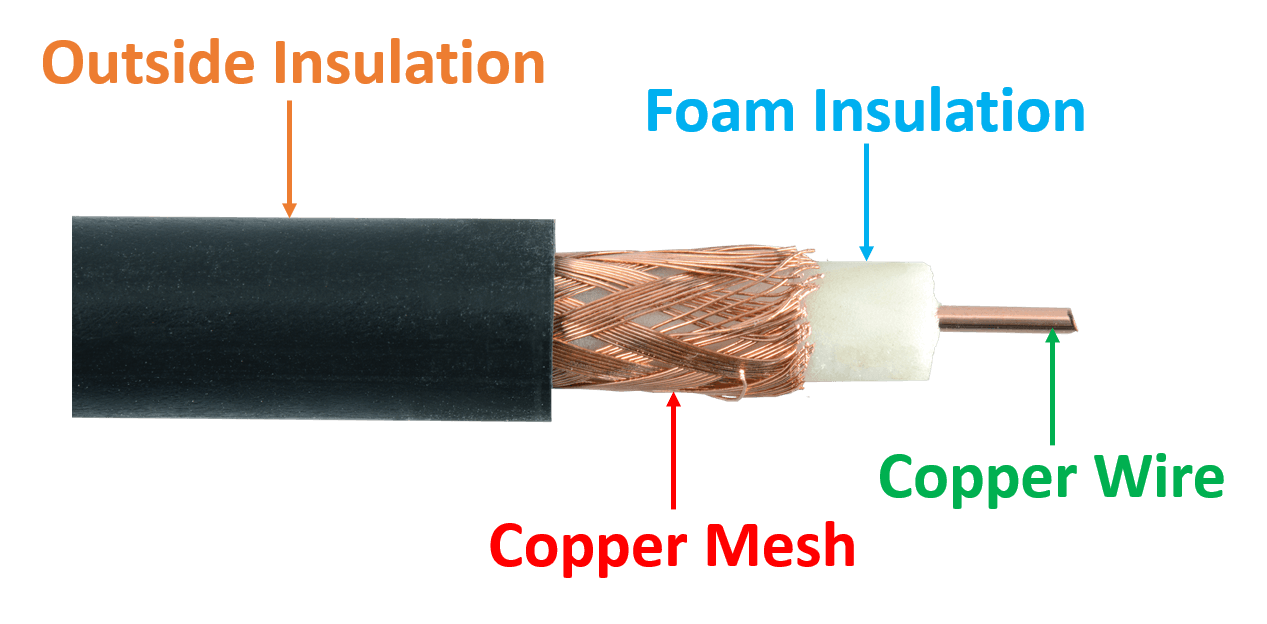
- The inner conductor of the coaxial cable is made up of copper, and the outer conductor is made up of copper mesh. The middle core is made up of non-conductive cover that separates the inner conductor from the outer conductor.
- The middle core is responsible for the data transferring whereas the copper mesh prevents from the EMI(Electromagnetic interference).
This type of cable connection is usually provided with a BNC connector.
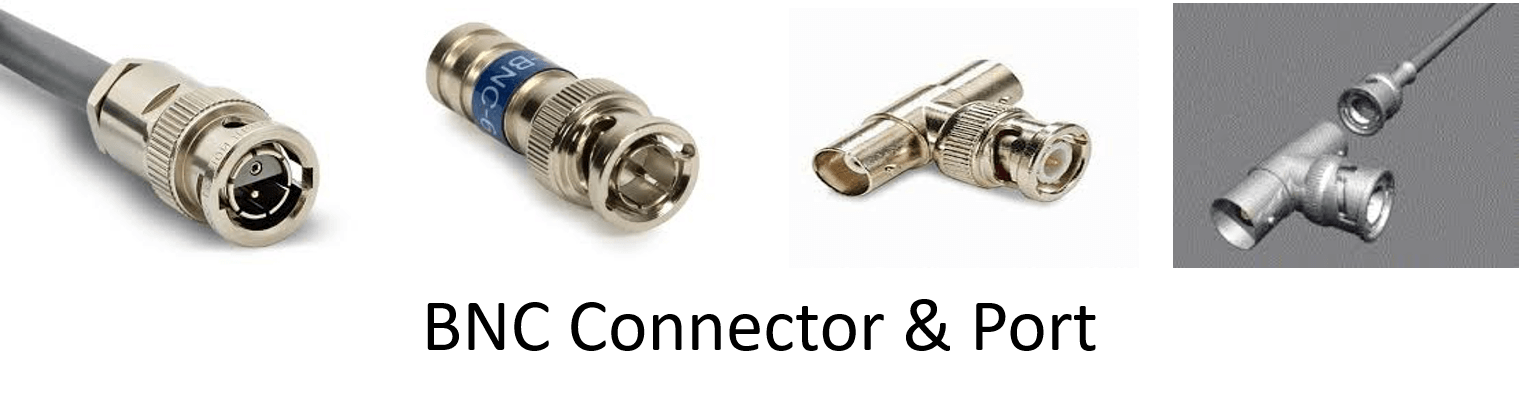


Types of Coaxial cable:
Co-axial cables are of two types. Such as:
Thin net:
Diameter: 0.25 inches
Transmission Distance: 185 m
Transmission Speed: 10Mbps
Thick net:
Diameter: 0.5 inches
Transmission Distance: 500 m
Transmission Speed: 10Mbps
Advantages of Coaxial Cable:
- Comparatively less data transmission loss.
- Its higher bandwidth makes it more suitable for video applications
- Can be used for both digital and analog data.
- Allows data transmission over longer (1km) distances.
Disadvantages of Coaxial Cable:
- Data transmission rate depends on the length of the cables.
- More expensive compared to twisted pair cables.
Usage of Coaxial Cable:
- Used for Cable TV network
- Used in CCTV Network
- Used in Local Area Network.
What is Optical Fiber Cable?
Fiber is the newest form of transmission cable technology. Instead of transferring data over copper wires, these cables contain optical fibers that transmit data via light, rather than pulses of electricity. Each optical fiber made with di-electric substant or crystal clear silica and multi-component glass material which is chemically neutral. and individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube, making it extremely resistant to external interference. The result is a very reliable and super fast connection that has 26,000X more transmission capacity than twisted-pair cables, but that also comes with a much higher cost.
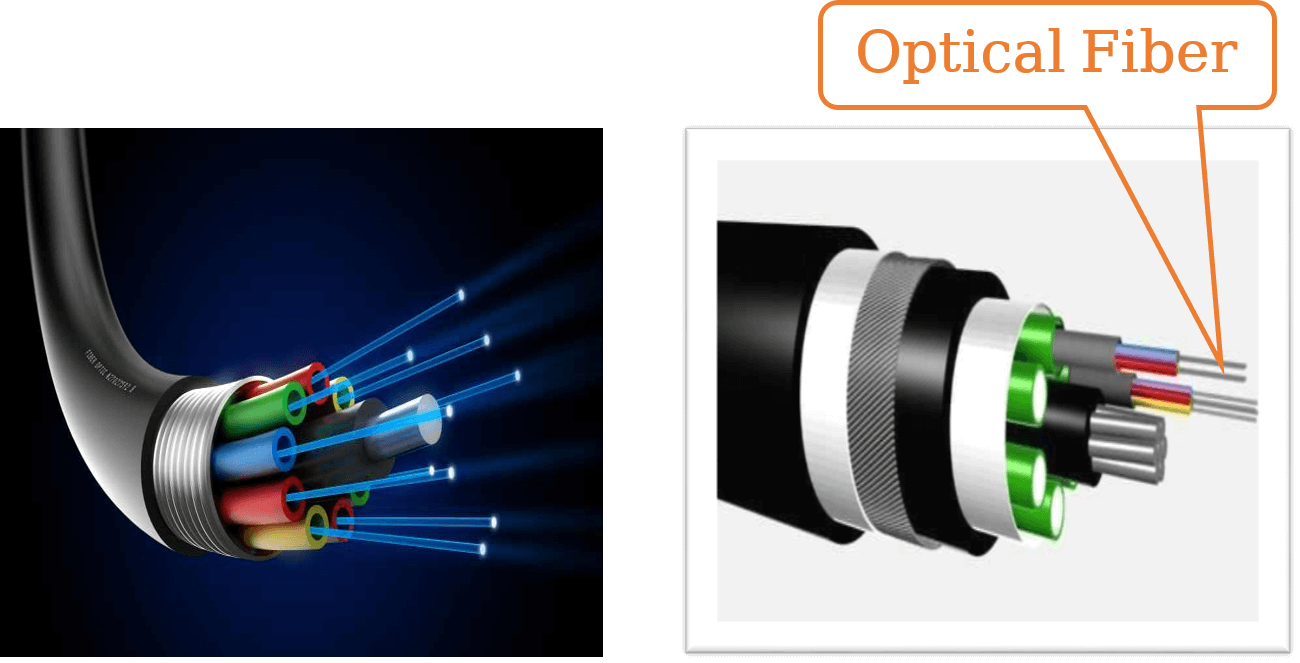
Data can be transmitted very fast through full internal reflection of light through optical fiber. Since optical fiber is a glass fiber, it is free from electromagnetic effects. The optical fiber currently available has a data transmission rate of 100 mbps to 2 gbps.
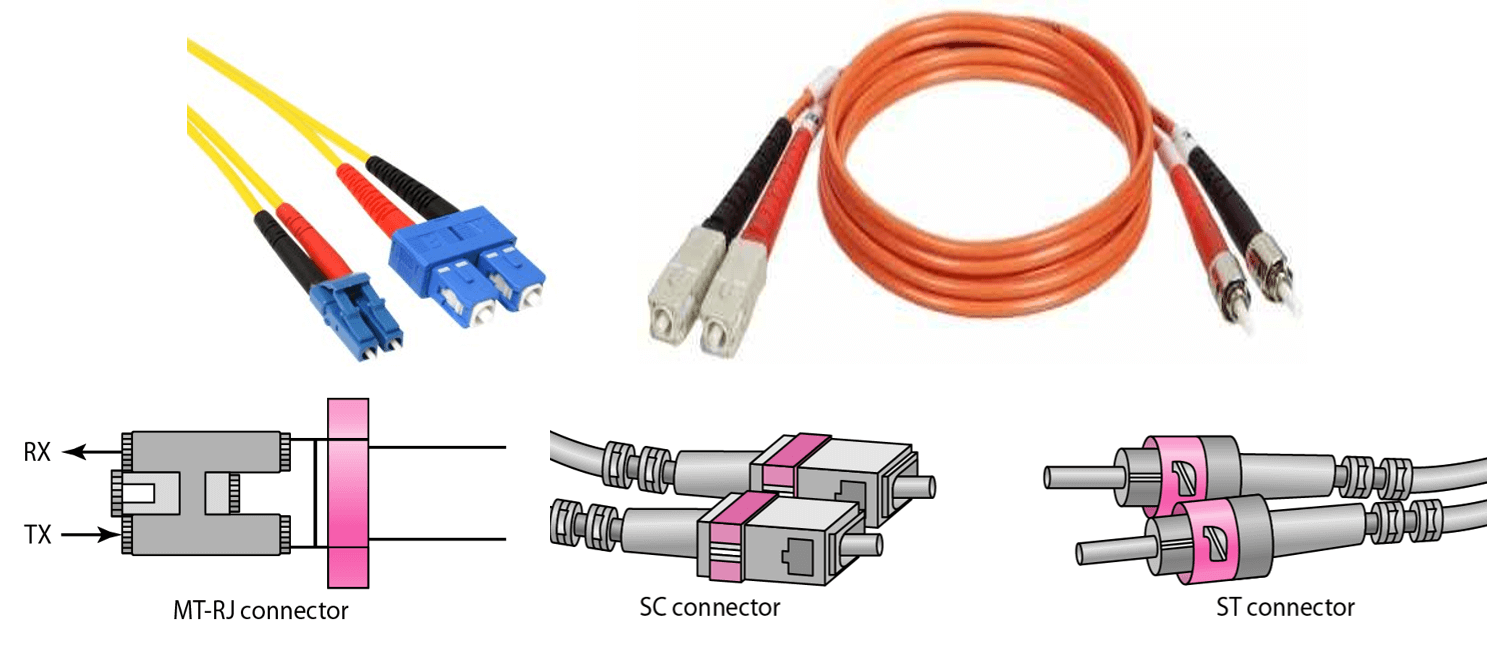
Connection to the device is provided with the help of SC-connector, ST-connector, MT-RJ-connector.
Basic Elements of Optical Fiber Cable:
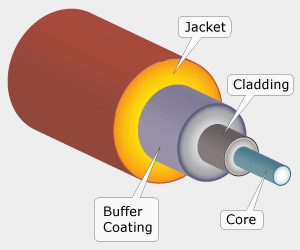
Core:
The optical fiber consists of a narrow strand of glass or plastic known as a core. A core is a light transmission area of the fiber. The more the area of the core, the more light will be transmitted into the fiber.
Cladding:
The concentric layer of glass is known as cladding. The main functionality of the cladding is to provide the lower refractive index at the core interface as to cause the reflection within the core so that the light waves are transmitted through the fiber.
Buffer:
Protects the fiber from the harmful effects of the external environment.
Jacket:
The protective coating consisting of plastic is known as a jacket. The main purpose of a jacket is to preserve the fiber strength, absorb shock and extra fiber protection.
Types of Optical Fiber Cable
There are two types of fiber optic cable based on core diameter. Such as:
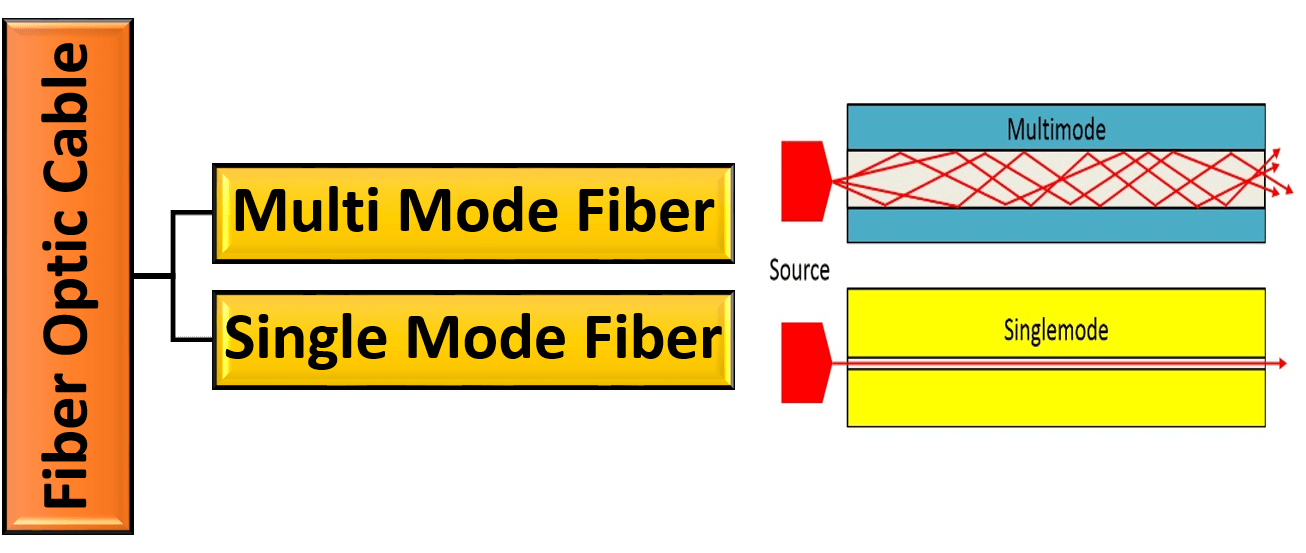
Single mode:
- Diameter of single mode fiber optic cable is 8-10 micron
- Has a small core and only allows one mode of light to propagate at a time
- Because of this, the number of light reflections decrease as they pass through the core
- The result is low attenuation and data that is able to travel further and faster
- Commonly used in telecom, CATV networks, and Universities.
Multimode:
- Diameter of Multi mode fiber optic cable is 50-100 micron
- Has a larger core diameter that lets multiple modes of light propagate
- The amount of light reflections increase as they travel through the core, which allows more data to pass through
- Because of its high dispersion, multimode cables have lower bandwidth, higher attenuation and reduced signal quality further it travels
- Most commonly used for communication over short distances such as LAN, security systems, and general fiber networks.
Multimode Fiber Optic Cable again two types:
Step-index fiber: Step index multimode fiber optic has uniform core refracting index.
Graded-index fiber: Core refracting index of Graded index multimode fiber optic is gradually decreased from center to outward.
Characteristics of Optical Fiber Cable
1. It transmits light signal instead of electrical signal.
2. Chemical stabilization or neutral.
3. It transmits light from the data source to the destination in a complete internal reflection mode.
Advantages of Optical Fiber Cable
1. Data can be transferred to very long distance (100 km) with high speed (gigabit range +).
2. The cable is light weight and very thin.
3. Less energy wastage.
4. Free from EMI.
5. Not influenced by temperature or pressure of the environment.
6. The security and privacy of data storage is paramount.
Disadvantages of Optical Fiber Cable
1. Fiber optic cable cannot be bent in U shape.
2. Fiber optic cable is extremely expensive.
3. Fiber optic cables are relatively more difficult to install than other cables.
Uses of Optical Fiber Cable
1. Fiber optic cable is more used as the backbone of the network.
2. At present, lighting, sensors and image editing are done through fiber optic cable.
3. Used to connect one country with another country or one continent with another continent through the seabed.
Lesson Evaluation-
Knowledge Based Questions:
a) What is twisted pair cable?
a) What is co-axial cable?
a) What is fiber optic cable?
Comprehension Based Questions:
b) Which cable is more effective in data communication-explain.
b) Explain the reason for using twist in twisted pair cable.
b) Why is fiber optic cable more effective in data transmission?
b) “Fiber optic cable is said to the backbone of network”-explain.
b) “It is possible to transfer data in the speed of light”-explain.
b) Why optical fiber is free from EMI?
b) Why fiber optic cable cannot be bent in U shape?
b) Explain the bandwidth of fiber optic cable.
b) Explain that data transmission is possible with the method of full internal reflection of light.
b) Explain the medium of data transmission in full internal reflection method.
b) Why multi component glass is used to make fiber optic cable? Explain.
Creative Questions:
Notice the following stem and answer the question:
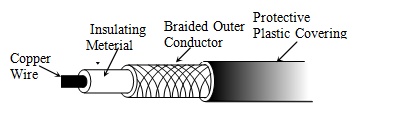
c) Describe each level marked in the figure.
d) Analyze the difference of the cable in the figure with the twisted pair cable.
Read the following stem and answer the questions:
ICT dependent knowledge and technology is leading people on the path to prosperity. Reading ICT, Arif learned about a medium of communication where sound as well as moving pictures can be sent. However, since the data cannot move in a crooked way, it is necessary to install a tower on a tall building with a frequency of 300MHz-300GHz. It was later combined with a newly invented technology that connected one continent to another through the ocean floor.
d) ‘The second medium is relatively convenient’ – Evaluate with logic.
Read the following stem and answer the questions:
A university IT officer created a network using twisted pair cables between different departments of the university. But he is not able to work properly as the data transfer on the network is slow. So he is thinking of using fiber optic cable instead of network cable.
c) Identifying the cause of network problem and explain.
d) Evaluate how reasonable the decision of the IT officer is?
Read the following stem and answer the questions:
Mr. Sajid has taken internet connection from an organization called “BDren”. The company used a cable to transmit data at the speed of light. As a result, Mr. Sajid can easily complete meetings with his various clients through video conferencing.
c) Describe the type of cable used in the stem.
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. As the wires are twisted, they are called-
a) Telephone cable
b) Co-axial cable
b) Twisted pair cable
d) Fiber optic cable
2. Which is the common color in twisted pair cable?
a) Orange b) Green c) Red d) White
3. Co-axial cable is divided into how many parts?
a) two b) three c) four d) five
4. Which of the following cable has the highest data transfer rate?
a) Shielded twisted pair cable
b) Un-shielded twisted pair cable
c) Co-axial cable
d) Fiber optic cable
5. Which cable is used for telephone?
a) Normal b) Twisted pair c) Co-axial d) Fiber optic
6. What is the normal rate of data transmission of co-axial cable?
a) 100 Mbps b) 200 Mbps c) 2 Gbps d) 40 Gbps
7. Which is the innermost part of optical fiber?
a) Buffer b) Core c) Jacket d) Cladding
8. Optical Fiber Cable are-
i. High speed Medium
ii. Cheap in price
iii. EMI free
Which one is correct?
a) i & ii b) i & iii c) ii & iii d) i, ii & iii
9. The advantage of optical fiber cable are-
i. This allows data to be transferred quickly
ii. It is easy to maintain
iii. It is free from EMI
Which one is correct?
a) i & ii b) i & iii c) ii & iii d) i, ii & iii
10. What is the function of photo detector?
a) Converting analog signals to digital signals
b) Converting electricity into light energy
c) Converting light energy into electricity
d) Converting digital signal to analog signal
Written by,
- Mizanur Rahman (Mizan)
- Lecturer in ICT, Shaheed Bir Uttam Lt. Anwar Girls’ College , Dhaka Cantonment
- Founder & Author at www.edupointbd.com
- Software Engineer at mands IT
- Former Lecturer in ICT, Cambrian College, Dhaka
- Contact: 01724351470
