At the end of this lesson-
- 1. You will be able to explain data and information.
- 2. You will be able to distinguish data over information.
- 3. You will be able to explain data hierarchy.
- 4. You will be able to explain the advantages and disadvantages of database.
- 5. You will be able to describe the application areas of database.
Data: Data is raw, unorganized facts that need to be processed. For getting desired output in a processing data is used as input. Data can be defined as a representation of facts and it is the smallest part of information. Data is represented with the help of characters such as alphabets (A-Z, a-z), digits(0-9) or special characters (+,-,/,*,<,>,= ).
Classification of data:
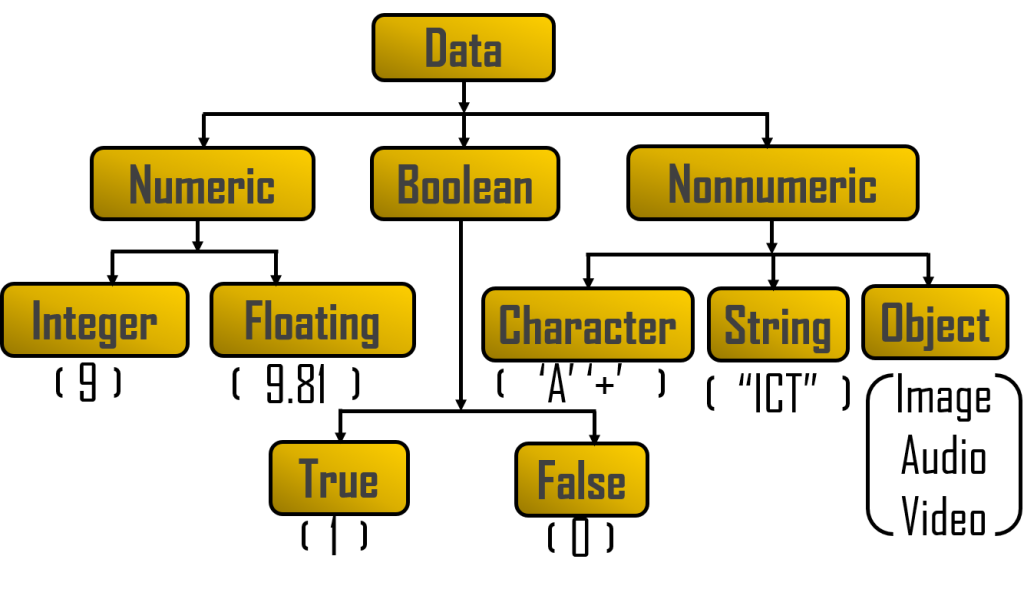
Information: When data is processed, organized, structured or presented in a given context so as to make it useful, it is called information. Information is the processed data on which decisions and actions are taken.
Examples of data and information: The marks of every subject of a student is called data. On the other hand, the report or result of a student by calculating the marks of all subjects is called information.
![]()
Difference between data and information:
| Data | Information |
| For getting desired output in a processing data is used as input. | Information is the processed data on which decisions and actions are taken. |
| Data is a single concept. | Information is a collective concept. |
| Data doesn’t give a complete idea about an object. | Information gives a complete idea about an object. |
| Data cannot be used directly. | Human being use information directly according to their needs. |
| There are some classifications of data. | There is no such classification of information. |
Database: A database is an organized collection of related data, stored and accessed electronically. A database is used by an organization as a method of storing, managing and retrieving information. Modern databases are managed using a database management system (DBMS). It may have single or related multiple tables in a database.
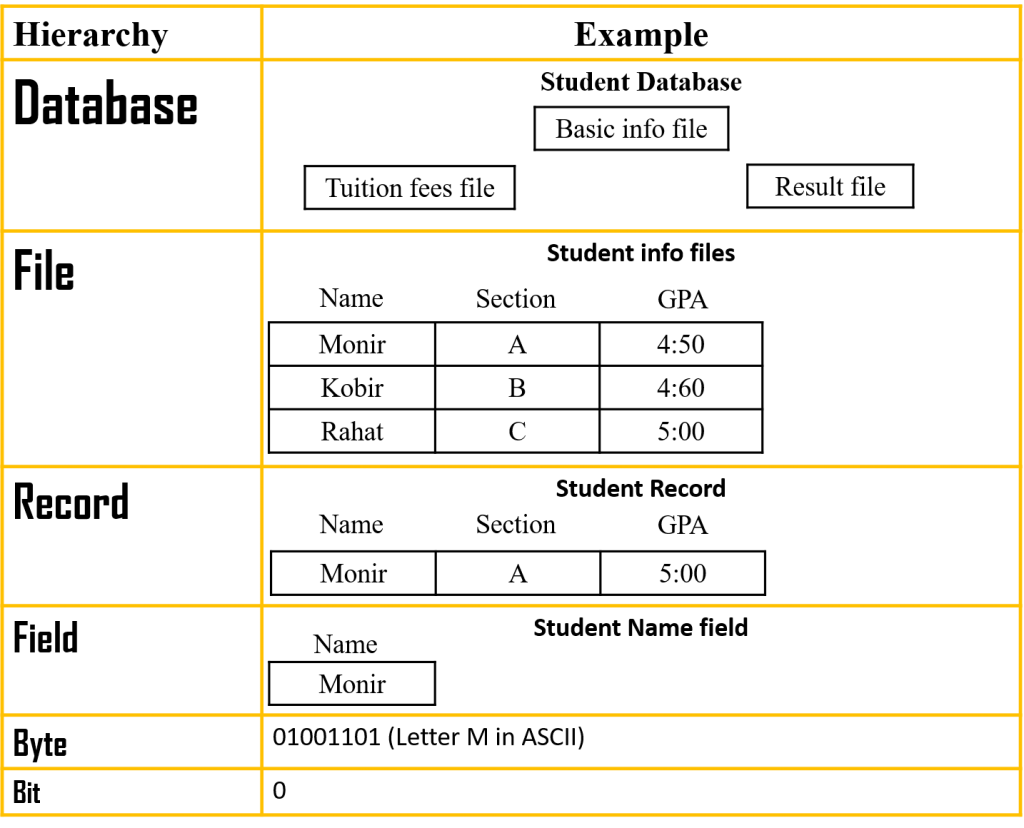
Data Hierarchy: Data hierarchy is a systematic organization of data mainly in a hierarchical form. Data organization basically involves bit, byte, field, record, file, and database.

Advantages of database:
- 1. Reduced data redundancy.
- 2. Reduced updating errors and increased consistency.
- 3. Greater data integrity and independence from applications programs.
- 4. Improved data access to users through use of host and query languages.
- 5. Improved data security.
- 6. Reduced data entry, storage, and retrieval costs.
- 7. Facilitated development of new applications program.
Disadvantages of database:
- 1. Database systems are complex, difficult, and time-consuming to design.
- 2. Substantial hardware and software start-up costs.
- 3. Damage to database affects virtually all applications programs.
- 4. Extensive conversion costs in moving form a file-based system to a database system.
- 5. Initial training required for all programmers and users.
Application areas of database:
- 1. Banking
- 2. Airlines
- 3. Library
- 4. Educational Institution
- 5. Credit Card
- 6. Telecommunication
- 7. Production and distribution
- 8. Human Resource (HR)
- 9. Automated Teller Machine (ATM)
- 10. Stock/Share Market
Lesson Evaluation-
Knowledge Based Questions:
- a. What is data?
- a. What is information?
- a. What is database?
- a. What is data hierarchy?
Comprehension Based Questions:
Creative Questions:
Multiple Choice Questions:
Written by,
- Mizanur Rahman (Mizan)
- Lecturer of ICT, Shaheed Bir Uttam Lt. Anwar Girls’ College ,Dhaka Cantonment
- Author at www.edupointbd.com
- Software Engineer at mands IT
- Former Lecturer of ICT, Cambrian College, Dhaka
- Email: mizanjust@gmail.com
- Cell: 01724351470
