At the end of this lesson-
- 1. You will be able to explain IP address.
- 2. You will be able to differentiate IPV4 and IPV6.
- 3. You will be able to describe different parts of URL or web address.
Go for Bangla Version
IP address:
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a logical numeric address that is assigned to every single computer, printer, switch, router or any other device of a TCP/IP-based network.
An IP address is a logical address that is used to uniquely identify every node in the network. Because IP addresses are logical, they can change.
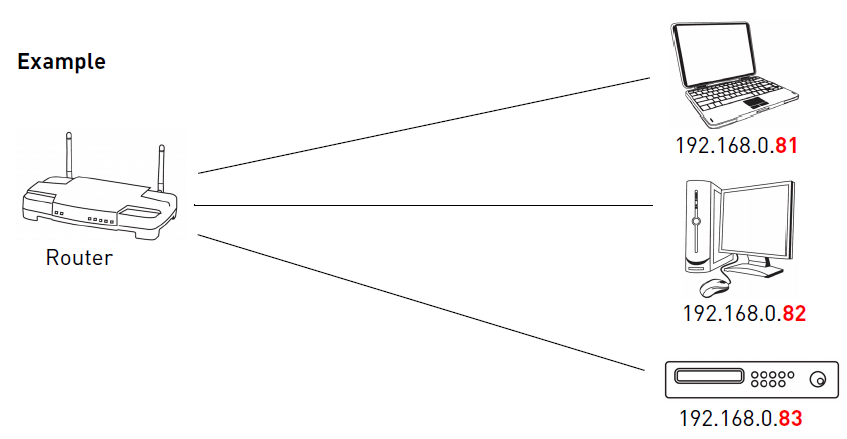
The numerals in an IP address are divided into 2 parts:
- The network part specifies which networks this address belongs to and
- The host part further pinpoints the exact location.
There are two primary types of IP address formats used today:
- IPv4
- IPv6.

IPv4:
- IPV4 stands for Internet Protocol Version-4.
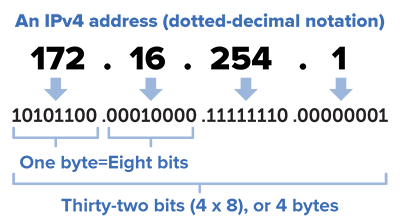
- IPv4 uses 32 binary bits to create a single unique address on the network.
- An IPv4 address consist of four sets of numbers from 0 to 255, separated by three dots.
- Each number is the decimal (base-10) representation for an eight-digit binary (base-2) number, also called an octet.
- For example: 216.27.61.137
- The total number of IPv4 addresses ranges from 000.000.000.000 to 255.255.255.255.
- There are 232 or 4,294,967,296 possible IP addresses.
- While this may seem like a large number, it is no longer enough to cover all the devices connected to the Internet around the world.
- Therefore, many devices now use IPv6 addresses.
IPv6:
- IPv6 stands for Internet Protocol Version-6.
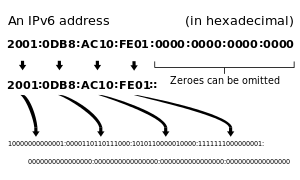
- IPv6 uses 128 binary bits to create a single unique address on the network.
- An IPv6 address is expressed by eight groups of hexadecimal (base-16) numbers separated by colons
- For example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652.
- Groups of numbers that contain all zeros are often omitted to save space, leaving a colon separator to mark the gap (as in 2001:cdba::3257:9652).
- There are 2128 or 3.4 x 1038or 340 undecillion) possible IPv6 addresses, meaning we shouldn’t run out of IPv6 addresses anytime soon.
Static Versus Dynamic IP Addresses:
IP addresses are assigned in two different ways. They may be dynamically assigned (they can change automatically) or statically assigned (they’re intended not to change, and must be changed manually). Most home networks use dynamic allocation.
An IP address can be static or dynamic. A static IP address will never change and it is a permanent Internet address. A dynamic IP address is a temporary address that is assigned each time a computer or device accesses the Internet.
IP address classes:
With an IPv4 IP address, there are five classes of available IP ranges: Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D and Class E, while only A, B, and C are commonly used. Each class allows for a range of valid IP addresses, shown in the following table.
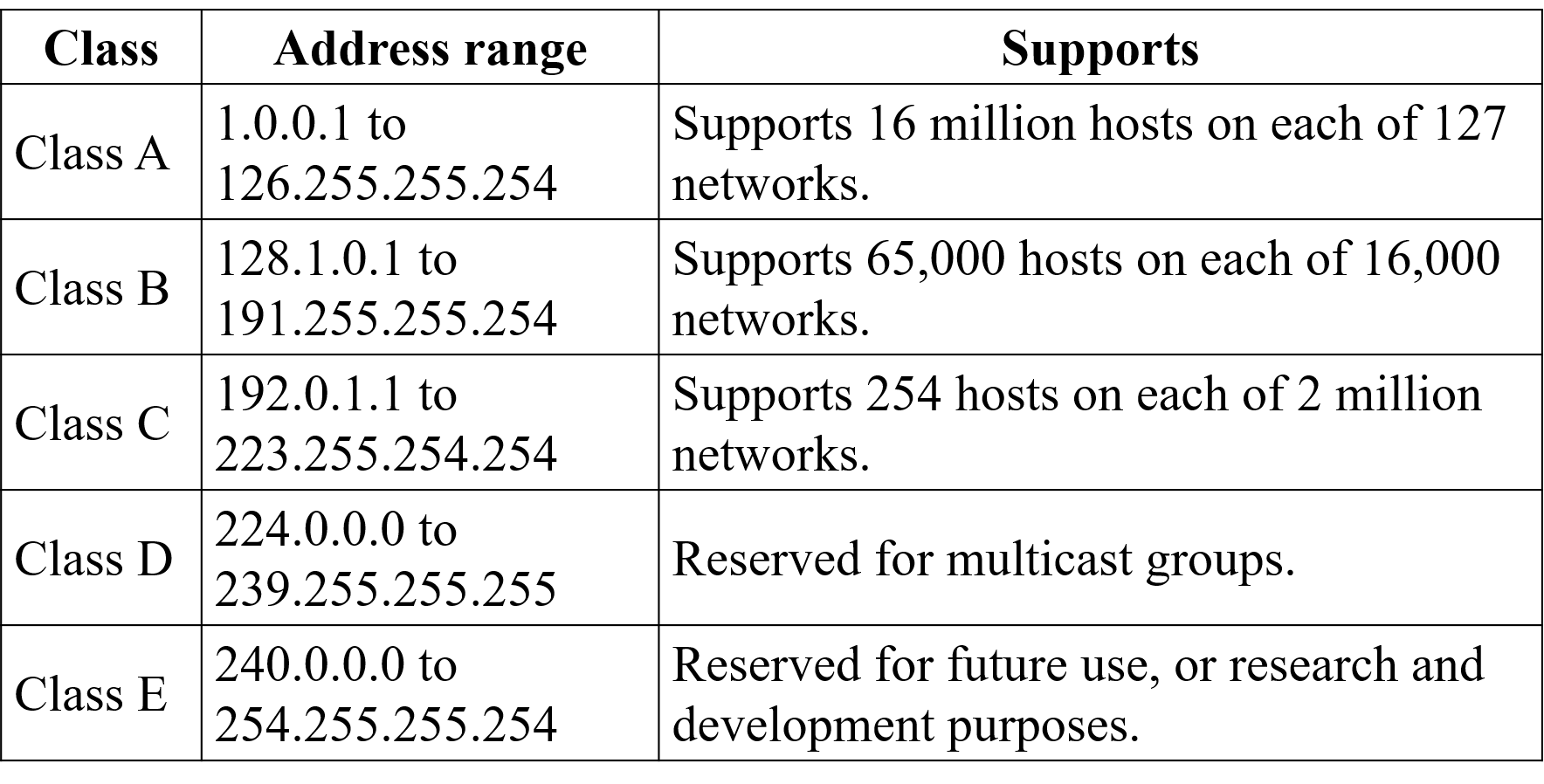
Ranges 127.x.x.x are reserved for the loopback or localhost, for example, 127.0.0.1 is the loopback address. Range 255.255.255.255 broadcasts to all hosts on the local network.
Web address or URL:
A web address, also known as a URL (Uniform Resource Locator), is a reference to a web resource that points to a location where a file, directory or website is hosted. Website addresses can represent the home page of a website, a script, image, photo, movie or other file made available on a server for viewing, processing or download. A website address begins with the protocol, a unique name and the domain and ends with a port number. Website addresses are entered into the address bar of an Internet browser. This name translates, through a DNS server to a unique number called an IP address. A URL-
http://hsc.edupoint.com.bd/ict/robotics.html
Different parts of a URL:
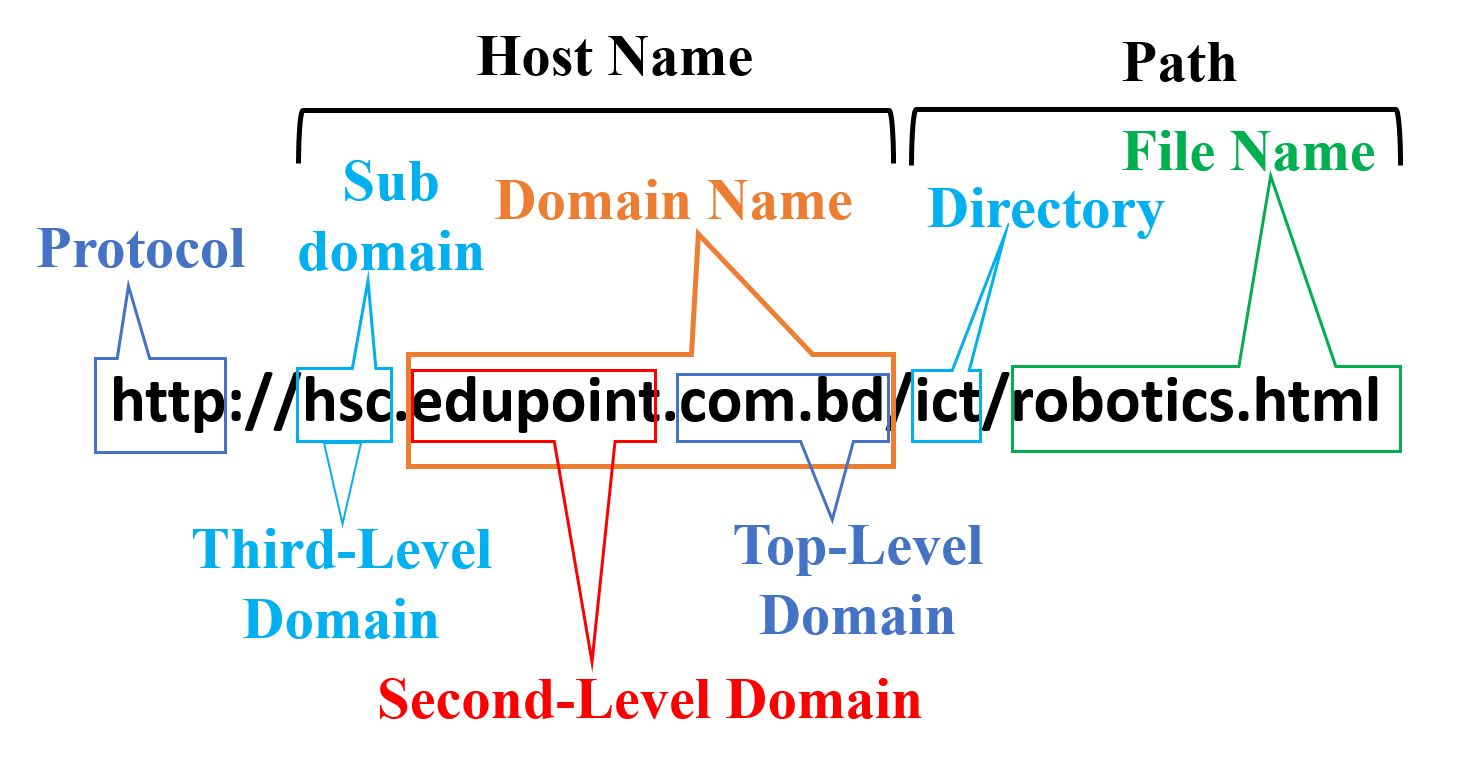
Protocol:
A protocol or scheme is a set of rules and guidelines for communicating data. Rules are defined for each step and process during communication between two or more computers.
HTTP of the above URL is the underlying protocol used by the World Wide Web and this protocol defines how messages are formatted and transmitted, and what actions Web servers and browsers should take in response to various commands. There are also other protocols such as-
- HTTP – Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
- HTTPS- Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure
- FTP – File Transfer Protocol
- IP – Internet Protocol
- TCP- Transmission Control Protocol
Domain Name:
A domain name is the textual address by which Internet users can access websites. A domain name that represents IP address. A domain name is used for finding and identifying server computers on the Internet. Server computers use IP addresses, which are a series of number. However, it is difficult for humans to remember series of number. Because of this, domain names were developed and used to identify entities on the Internet rather than using IP addresses. DNS (Domain Name System) server is an Internet service that translates domain names into IP addresses.
The domain name must be registered before you can use it. Every domain name is unique. No two websites can have the same domain name.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers(ICANN) is an American nonprofit organization that controls domain names around the world.
Every domain name has two main parts and an optional part. They are:
- Second-level Domain
- Top-level Domain
- Third-level Domain or Sub-Domain (Optional)
Second-level Domain: Second-level Domain is usually consistent with the name of the organization. Second-level Domain is also called Domain. No space or special characters (@, &, %, $, # etc.) can be used for domain naming. Only letters and numbers can be used. The characters used in the domain are not case sensitive.
Top-level Domain: Top-level domain (TLD) refers to the last segment of a domain name, or the part that follows immediately after the “dot” symbol.
A top-level domain recognizes a certain element regarding the associated website, such as its objective (business, government, education), its owner, or the geographical area from which it originated.
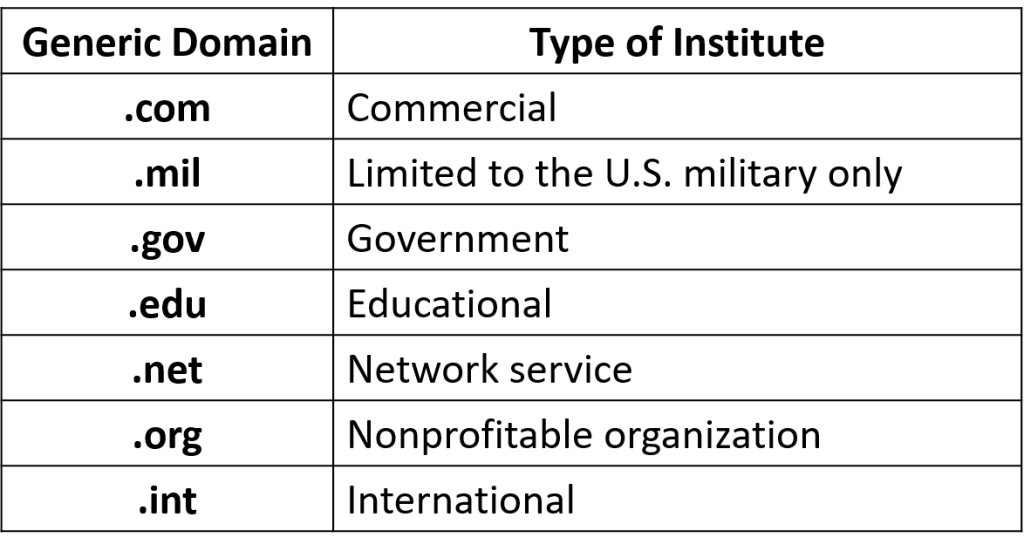
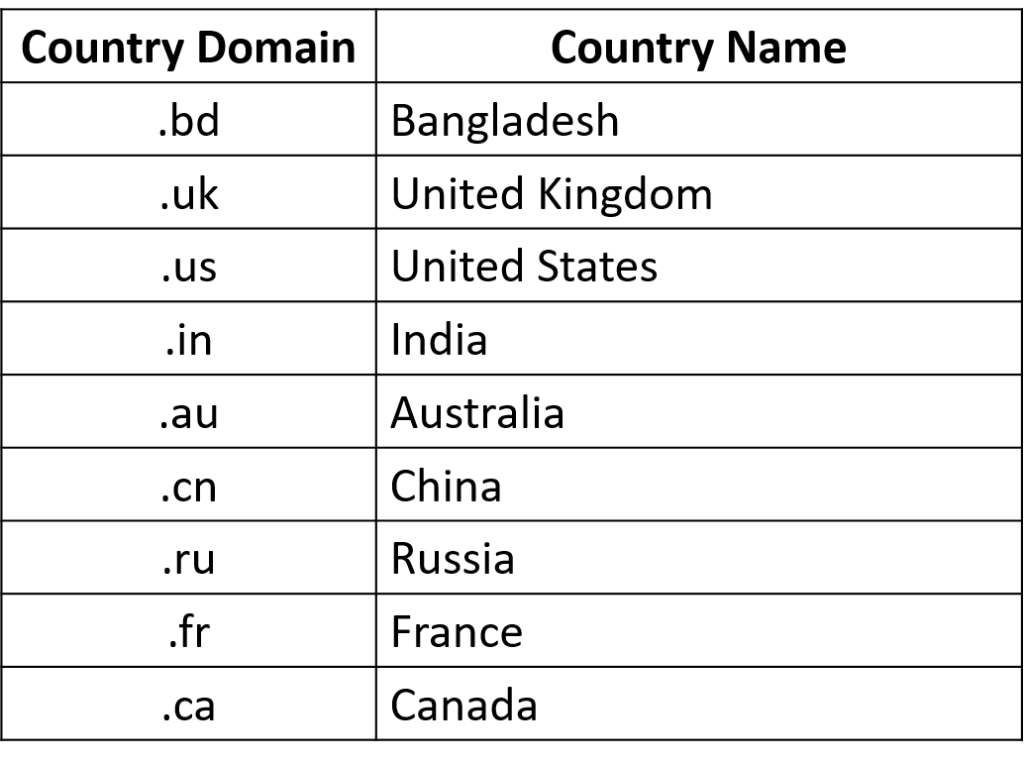
TLDs are mainly classified into two categories:
- Generic Domain
- Country Domain
Generic Domain: It recognizes a certain element regarding the associated website, such as its objective business, government, education etc.
Country Domain: It recognizes websites owner, or the geographical area from which it originated. It is an optional part of a domain.
Third-level Domain or Sub-Domain: A sub-domain is an additional part to the main domain. Sub-domains are created to organize and navigate to different sections of the website. You can create multiple sub-domains or child domains on your main domain. It is considered a third-level domain used to organize site content.
For example – www.google.com is a domain and maps.google.com is a sub-domain of it.
Directory: The path identifies the specific resource in the host that the web client wants to access. For example, “ict”in the above URL.
File Name: It indicates the name of web pages or web resources. In the above URL, robotics.html is the name of a web page.
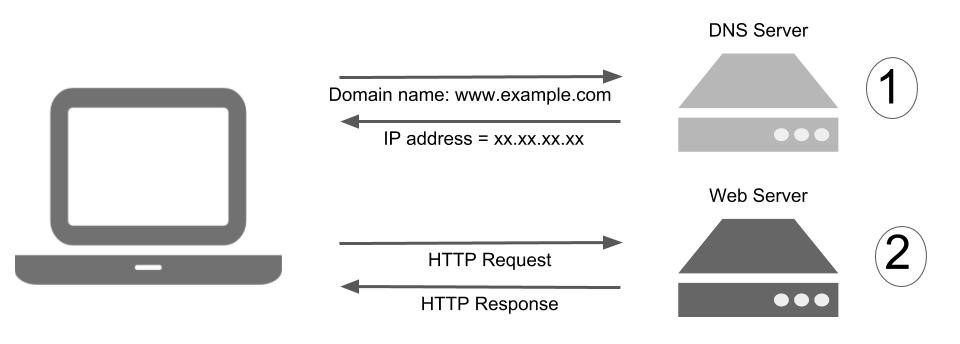
DNS Server:
DNS (Domain Name System) server is an Internet service that translates domain names into IP addresses. Because domain names are alphabetic, they’re easier to remember. The Internet however, is really based on IP addresses. For example, when a Web address (URL) is typed into a browser, DNS servers return the IP address of the Web server associated with that name.
The DNS system is, in fact, its own network. If one DNS server doesn’t know how to translate a particular domain name, it asks another one, and so on, until the correct IP address is returned.
Lesson Evaluation-
Knowledge Based Questions:
- a. What is web address / URL?
- a. What is IP address?
- a. What is domain name?
- a. What is protocol?
- a. What is HTTP/HTTPS/FTP/TCP?
- a. What is DNS server?
Comprehension Based Questions:
- b. Why domain name needs to be registered? explain.
- b. Explain the importance of domain name.
- b. “Domain of a website should be related to the institute” explain.
- b. Why there is WWW in domain name? explain.
- b. Explain top-level domain.
- b. “It is not possible a web address without top-level domain”-explain.
- b. “Domain name is more convenient to use than IP address” -explain.
- b. Explain 121.235.101.11 .
Creative Questions:
Read the following stem and answer the question:
http://www.kgmc.gov.bd/2015/recruit.html
c) Identify and explain the different parts of the stem.
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. What is the organization that controls domain names around the world?
a) ICANN b) ICCNN c) CCNA d) ISDN
2. What is the full form of http?
a) Hyper Text Tranmit Protocol
b) Hyper Time Tranmit Protocol
c) Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
d) Hyper Term Transfer Protocol
3. What is the full form of URL ?
a) Uniform Resource Locator
b) Uniform Resource Line
c) Unicode Resource Locator
d) Unique Resource Line
4. http://www.bulbulcse.com here what is indicated by bulbulcse ?
a) Protocol b) File c) Domain name d) Directory
5. The next part of the @ sign in the e-mail address is-
a) User Name b) Domain Name c) Host Name d) Protocol
6. Data is exchanged between server and client computer through which?
a) IP Address b) Search Engine c) html d) http
7. At the beginning of each web address there is –
a) www b) http c) html d) FTP
8. How many bits in IP Address?
a) 8 b) 16 c) 32 d) 64
9. Different parts of URL are-
i. Protocol ii. Host Name iii. Directory or File Name
Which one is correct?
a) i & ii b) i & iii c) ii & ii d) i, ii & iii
10. Country Domain are –
i. ac ii. au iii. jm
Which one is correct?
a) i & ii b) i & iii c) ii & ii d) i, ii & iii
11. https://www.facebook.com, Here what is indicated by s?
a) Server b) Security c) Services d) Save
12. What is the last part of http://www.yahoo.com ?
a) Protocol b) Domain name c) File name d) Domain Type
13. What is the total number of octets required to publish an IP address?
a) 2 b) 4 c) 8 d) 32
14. What is said the address of the webpage?
a) URL b) HTTP c) HTML d) WWW
15. What is the full form of DNS?
a) Domain Name Server
b) Domain Name System
c) Domain Number System
d) Domain Number of Server
16. Domain Name is-
a) A unique name for the website
b) Name of the server
c) Web file name
d) The name of the folder
17. What is the full form of www?
a) World Wide Web
b) Word Wide Web
c) Wireless Wide Web
d) Wide Wireless Web
Written by,
- Mizanur Rahman (Mizan)
- Lecturer of ICT, Shaheed Bir Uttam Lt. Anwar Girls’ College , Dhaka Cantonment
- Author at www.edupointbd.com
- Software Engineer at mands IT
- Formar Lecturer of ICT, Cambrian College, Dhaka
- Email: mizanjust@gmail.com
- Cell: 01724351470
